ASK RFID Reader (for ISO11785)
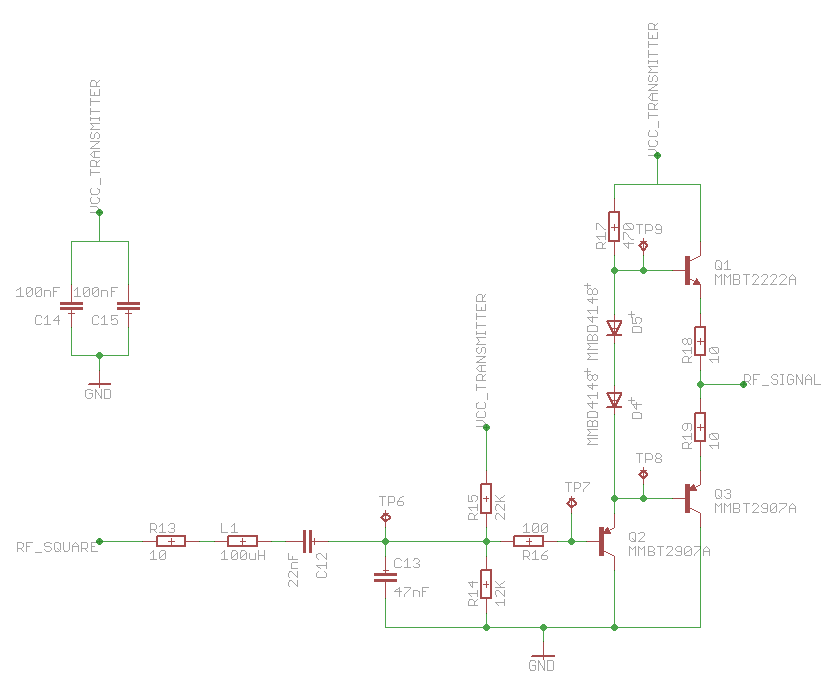
The ASK reader that I implemented in my solution looked like this after drawing in all the components in Eagle:The overall system can be split into two, the transmitter part, and the receiver part. The top-right most part of the circuit is the transmitter.
Transmitter
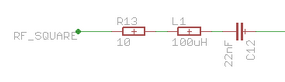
The transmitter is a simple current amplifier, where the transistors Q1 and Q3 will alternately pull the antenna voltage high and low depending on the "control" signal in to the amplifier, thus forcing a high current through the antenna. The important thing to note is that this circuit does not generate any frequency signal on itself, it requires a source that produces the correct frequency, the carrier frequency in this case. For the original implementation from the Microchip application note this circuit was tunes to receive a 125 kHz signal, to generate the correct carrier frequency for 125 kHz RFID tags. In my implementation I had to change this to 134.2 kHz since this is the carrier frequency of the Animal RFID standard. The way to do this is to try to further identify the different parts of the system.A trained RF designer will probably already noticed the band pass filter in front of the amplifier:
Where the L1 and C12 defines the band pass center frequency and the R13 defines the width of the filter. In the original implementation the values for L1 and C12 was tuned to, more or less, exactly 125 kHz. In this implementation this has been tuned to more closely match 134.2 kHz using the formula:
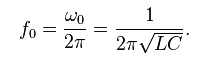 | ||
| Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LC_circuit |
Having this input filter basically means that any signals containing frequencies other than the center frequency are damped through the filter. This comes in handy when it comes to generating the actual frequency signal. An expensive way of generating this input frequency whould be to have a crystal that exactly match the intended frequency. But a much more affordable solution will be to use a frequency output of the MCU that is supposed to decode the signal in the other end anyway. So using a timer on e.g. an AVR XMEGA device to produce a frequency correct "PWM" signal at exactly 134.2 kHz will mean that the only cost to the solution will be to route out another signal from the MCU.
The challenge is that the digital on-off "PWM" signal (square wave signal) will contain much more frequencies than just the main/center frequency. This is due to the nature of rapidly changing signals, i.e. an infinite sharp change in voltage in the time domain, means en infinite wide response in the frequency domain, i.e. the signal contains an infinite amount of frequencies. Think of a lightning bolt, if you listen to the radio, or watch TV you can hear the lightning bolt as a tick or see it as a disturbance on the TV no matter what channel you are tune in on, this is because the lightning bolt is a very sharp change in the surrounding air voltage, causing it to transmit its signal across all channels and frequencies. This is quite a big subject in itself so I will not describe more in detail here how this works (for more information see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourier_transform). Long story short, a square wave signal will be dominated by the main/center frequency, but will also contain a considerable amount of 2x the frequency, 3x and so on. So what the band pass filter does is to filer out any other frequencies than the main/center frequency, giving a clean sine signal out as input to the amplifier. That way we know that will will not disturb the neighbors 8'o clock radio news, or your own cellphone signal, or your garage door opener and so on.
When it comes to the design of the filter, I have already mentioned the L (inductor) and C (capacitors) role, they decide the center frequency of the filter. The R (resistor) on the other hand decide the width of the filter (or band width), i.e. a higher R will cause the filter to accept more frequencies around the center frequency, and keep in mind that the filter is quite sensitive to small changes in R. The reason why we want a certain width of the filter is that using standard components it is often difficult to get exactly the correct frequency you need for your application. So in my circuit I use L = 100uH and C = 22nF which gives a center frequency of 107.302 kHz which is relatively far away from the desired 134.2 kHz, but using the R to increase the bandwidth of the filter means that it will work on 134.2 kHz as well. A small note worth looking into is that inductors could have high internal resistance, which means that the filter might become too wide and start including square parts of the input signal, which is unfortunate. Make sure to use inductors of a certain quality with a small internal resistance. The transmitter will be identical for different types of RFID standards, i.e. ASK (amplitude shift keying), FSK (frequency shift keying), PSK (phase shift keying), and so on.
Receiver
My implementation uses ASK (amplitude shift keying) as it is defined in the ISO11785, since that is the target of the application, to read the ear tags on sheep.ASK, or amplitude shift keying, means that the digital information is carried in the amplitude of the signal, where keys refer to the actual bit words, i.e. what defines a 1 and 0 in the signal transmission. The radio signal itself is more or less identical to what you see as AM on your car radio, on AM music, voice, etc. are transmitted using changes in the amplitude of the signal, vs. in the change of frequency as it is on a FM radio.
The receiver part consist of an input filter, envelope detector (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Envelope_detector) and operational amplifiers (OPAMP), which amplify and filter the signal further, lastly it uses one OPAMP to digitize the signal.
The clever thing with this design is that the antenna becomes part of the input filer as most RFID antennas are effectively inductors or coils of copper wire. This antenna is then put in series with a capacitor to form a band pass filter as the one for the transmitter where the center frequency is, in my case, 134.2 kHz.
Antenna design
For the antenna I picked up some copper wire from http://www.hobbyengineering.com (H04443-01P Enamel Magnet Wire 34 AWG), this works perfectly for winding RFID antennas. I typically use apps like the ElectroDroid to calculate the amount of turns based on the physical size of the antenna and match it with a standard capacitor value, but any other inductor calculator tool will do. The Androide one is just because it is convenient. The results are something like this:To tune the antenna I found that the easiest way was to hook one end of the antenna to a resistor and the other to the capacitor as shown in the schematic below, so that you now have a series network with a resistor, antenna (inductor), capacitor, and ground. Then I hooked a signal generator up to the top most pin of the resistor, and an oscilloscope to the other pin of the resistor:
The signal generator is put in sweep mode around the frequency we are targeting, e.g. 110 kHz to 170 kHz, a long enough time resolution on the oscilloscope will no show a dip of amplitude of the signal at exactly the point where the antenna inductor and capacitor are matched. Often signal generators have an output that will toggle a pin at a certain frequency, this comes in handy here, where this can be used to determine the exact frequency the circuit match. If one set this toggle to happen at the target frequency, e.g. 134.2 kHz and connect the input to another input on the oscilloscope it is easy to see if the current setup matches or not. If it does not match one have to start to either remove or add windings to the antenna. By continuing to add or remove windings until the the signal generator toggle and the lowest point of the amplitude of the output signal are exactly on the same spot one have a perfectly matched antenna.
Envelope detector
After the antenna the signal is fed into an envelope detector, that simply means that the carrier frequency, 134.2 kHz in this case, is filtered out, and you are left the the change in amplitude of the signal only on the positive side.The signal will swing around zero before entering the diode, where the amplitude will be equally far from zero on the positive side as the negative side. After the diode; the signal is filtered using a series of caps and resistors, the value of these caps and resistors are govern by the bit length, i.e. they have to smooth the signal enough for the carrier frequency, 134.2 kHz, to be filtered away, but fast enough to not filter away the bit information (high-low / low-high) in the amplitude signal. Next the signal is fed through 3 stages of operational amplifiers.
Operational amplifier
The first operational amplifier is in inverting configuration and has a gain of 1MOhm/22kOhm = 46.455 times, and has a low pass filter effect due to the 47pF capacitor. The two diodes are there to reduce the effect of fast changing signals, e.g. a spike due to static discharge. The idea is that if the voltage between the output and input of the opamp is above the threshold of the diode, typically 0.7V, it will be a short between the output and input effectively giving a gain of 1, and not 46. In that way voltage spikes will be damped through the system. I have found that these diodes are not necessary to make the circuit work, but it is always wise to have to possibility to add them if it turns out to be a problem.The positive side of the opamp is connected to the center voltage, the reason for this is that, at least in my application, negative voltage is not available. Typically operational amplifiers have a positive and negative power-supply, e.g. +12V and -12V, and the operational or working point will then be 0V. In this application the working point of the opamp has been moved upwards to half the supply voltage, that way one do not need the extra negative supply voltage, but of course one will have a smaller operational range of the opamp.
The next opam in the chain is very similar to the first one, and adds additional gain and filter to the signal. In this application I added a pot-meter to be able to control the gain of this second step, but I found that a value of 5kOhms are about correct. This gives a gain of this stage at 200 times.
The total gain in the system is now 200 * 46.455 = 9291 times. So if the system runs on 9V we will have a maximum input on the amplitude of the RF signal to 9V/2 (half the voltage due to the working point of the opamp) = 4.5V/9291 ~ 48mV. That way none of the opamps so far will go into saturation.
The last opamp stage is used a bit differently, here you want the opamp to saturate, either at the low end or at the high end.
If the input signal to this opamp is over the THRESHOLD it will output 9V (or the opamp high supply voltage), if the input signal is below it will output 0V.
The RF amplitude signal has now been demodulated through the envelope detector, filtered and amplified through two stages of operational amplifiers, and at the end digitized using the saturation properties of opamps. The last voltage divider has been added to reduce the voltage down to a level that is safe for the XMEGA MCU (3.3V) that reads the signal.
The next blog post in this series will be on decoding the actual digital signal using an Atmel ATxmega32A4U MCU.